The best part is that there are numerous options on how you are able to have a wonderful, worth it flooring. The sort of flooring you pick out for your basement will depend on individualized preference as well as possible environmental factors. Basement flooring has many types out in the market, which makes the choice fairly difficult.
Here are Images about Structural Basement Floor
Structural Basement Floor

Men and women are likely to focus big groups of people on the structural designs first (for great reasons!) and then when the project is actually wrapping up, the things like basement floor covering, paint and finishing touches are handled. The structural problems in a basement are a major deal clearly. You can paint the walls and match your basement flooring or vice versa, choose the basement flooring and paint the walls to complement.
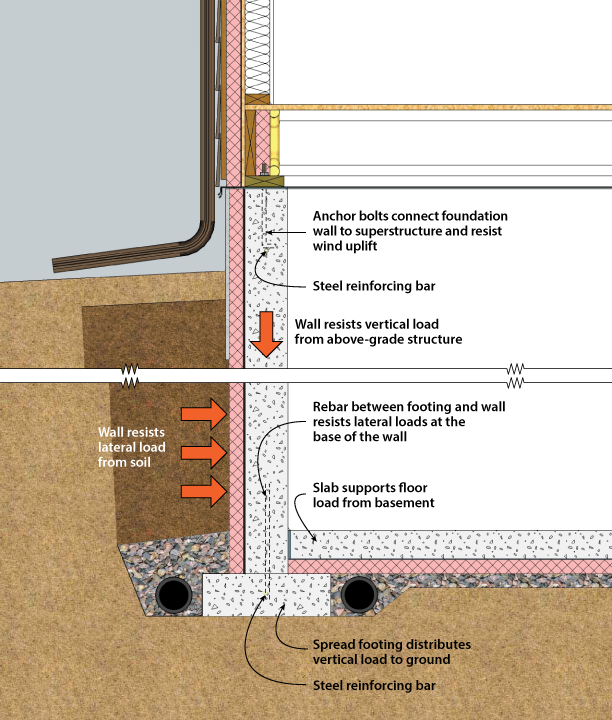
DOE Building Foundations Section 2-1 Structure
You have hardwood in the cooking area, dining area plus living area, floor tile in the bathtubs as well as carpet in the bedrooms. Another critical consideration when it comes to basement flooring is actually if who is carrying out the flooring work: you or a hired professional? If it's you, remember that tiles and stained basement floor normally takes more exertion to haul as well as install.
Images Related to Structural Basement Floor
0230-bw Lowering Basement Floors Bench Footing – Structure

Advanced Floor Concepts u003e Structural Floors u003e Concrete Floors

Rocky Mountain Steel Piering, Foundation Repair Littleton

Advanced Floor Concepts u003e Structural Floors u003e Concrete Floors
Advanced Floor Concepts u003e Structural Floors u003e Concrete Floors
Wood Floor Basements: WARMER, ALKALI RESISTENT, u0026 AFFORDABLE
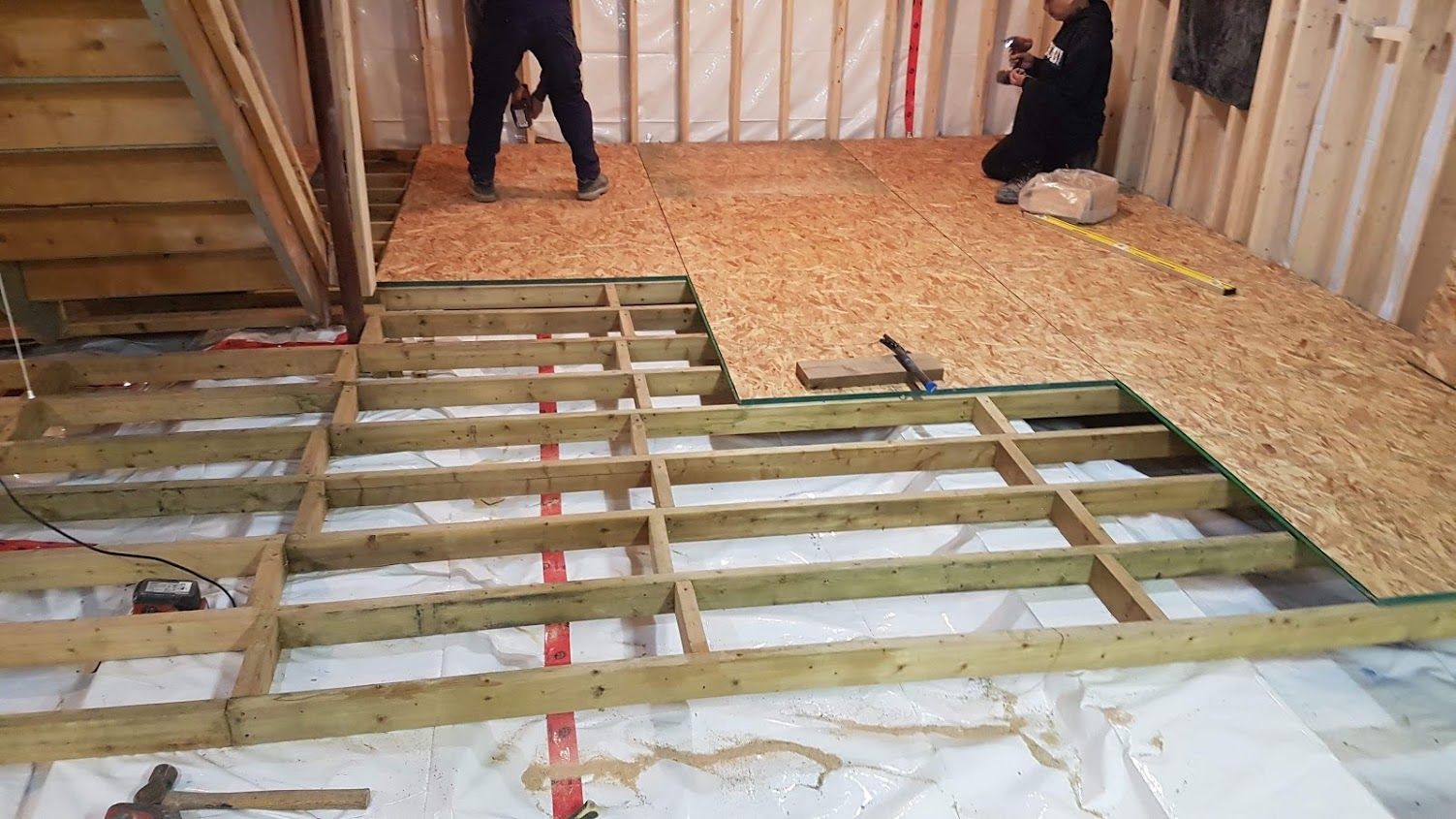

Wood Floor Basements: WARMER, ALKALI RESISTENT, u0026 AFFORDABLE
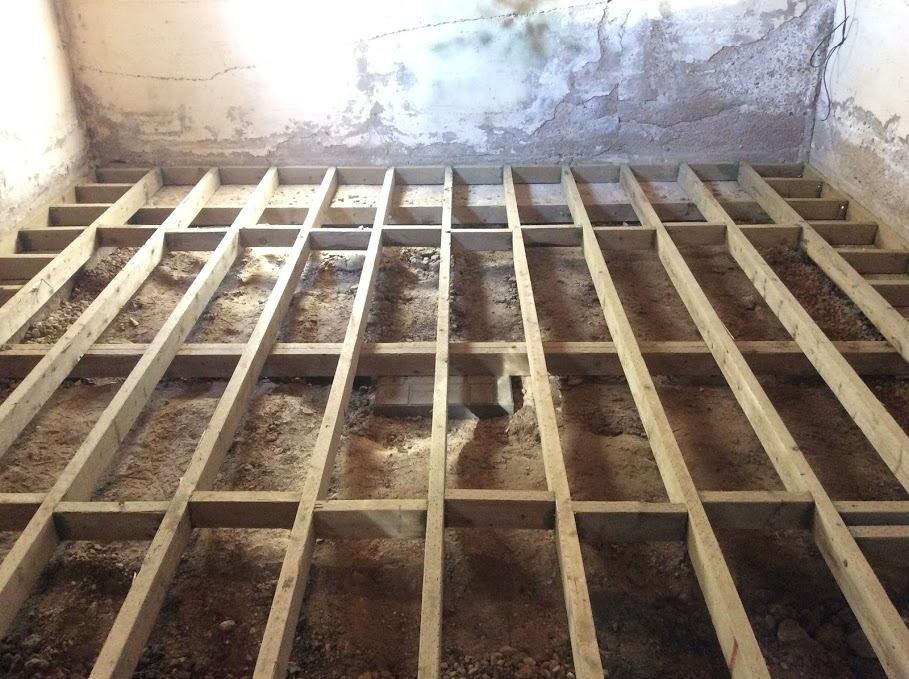

Rocky Mountain Steel Piering, Foundation Repair Littleton

Basement Construction – Types of Concrete Basements – Concrete Network

Advanced Floor Concepts u003e Structural Floors u003e Concrete Floors

0231-bw Lowering Basement Floors Underpinning – Structure

Advanced Floor Concepts u003e Structural Floors u003e Steel Joist w/Wood
Related articles:
- Asbestos Floor Tiles In Basement
- Basement Floor Cracks Seeping Water
- One Floor House Plans With Walkout Basement
- Sample Basement Floor Plans
- Rubber Flooring For Basement Reviews
- Concrete Basement Floor Coatings
- Best Flooring For A Basement That Floods
- Vinyl Tile On Concrete Basement Floor
- Carpet On Concrete Basement Floor
- Basement Flooring Squares
A structural basement floor is a crucial component of any building’s foundation. It provides support for the entire structure above it, as well as protection against moisture and other environmental factors. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of a structural basement floor, including its construction, materials, maintenance, and common issues.
Construction of a Structural Basement Floor:
The construction of a structural basement floor typically begins with excavating the area where the basement will be located. This excavation is necessary to create a level surface on which to pour the concrete slab that will serve as the floor. Before pouring the concrete, it is essential to install a layer of gravel or crushed stone as a base to promote proper drainage and prevent moisture from seeping into the floor.
Once the base is in place, forms are used to contain the concrete while it is poured and shaped to create a level surface. Reinforcing steel bars, known as rebar, are often added to provide additional strength and prevent cracking. The concrete is then left to cure and harden before any further construction can take place.
FAQs:
1. Why is it important to use reinforcing steel bars in the construction of a structural basement floor?
Reinforcing steel bars help to strengthen the concrete and prevent cracking, ensuring that the basement floor can support the weight of the structure above it.
2. How long does it take for concrete to cure and harden before construction can continue?
The curing process typically takes about 28 days, although some types of concrete may reach sufficient strength sooner.
Materials Used in Structural Basement Floors:
Several materials are commonly used in the construction of structural basement floors, with concrete being the most popular choice due to its durability and strength. However, other materials such as epoxy coatings and rubber membranes may be used to provide additional protection against moisture and improve the overall longevity of the floor.
Concrete floors can be finished in various ways, including staining, polishing, or adding decorative patterns or textures. These finishes not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of the floor but also provide an additional layer of protection against wear and tear.
FAQs:
3. Are there any alternatives to using concrete for a structural basement floor?
While concrete is the most commonly used material for basement floors, epoxy coatings and rubber membranes can also be effective options for certain applications.
4. How long can I expect a properly constructed structural basement floor to last?
With proper maintenance and care, a well-constructed basement floor can last for decades without needing major repairs or replacement.
Maintenance of Structural Basement Floors:
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring that a structural basement floor remains in good condition over time. This includes regular cleaning to remove dirt and debris that can cause abrasion or staining, as well as periodic inspections for signs of damage or wear.
Sealing or waterproofing the floor can help prevent moisture from seeping through and causing issues such as mold growth or deterioration of the concrete. It is also important to address any cracks or chips in the floor promptly to prevent them from expanding and causing more significant problems.
FAQs:
5. How often should I seal or waterproof my structural basement floor?
Sealing or waterproofing should be done every 1-2 years, depending on the level of traffic and exposure to moisture that the floor experiences.
6. What should I do if I notice cracks or chips in my basement floor?
Small cracks or chips can usually be repaired with epoxy filler or patching compound. Larger cracks may require professional repair to ensure that they do not compromise The structural integrity of the floor.


