A number of years ago individuals started to recognize they'd a useful extra room which, using the application of some gyprock to the wall surfaces as well as ceiling, some color and some form of basement flooring, may be turned to an extra living room or perhaps rooms. Take your schedule and find out precisely what you need to complete to fix your floor.
Here are Images about How Thick Are Basement Floors
How Thick Are Basement Floors
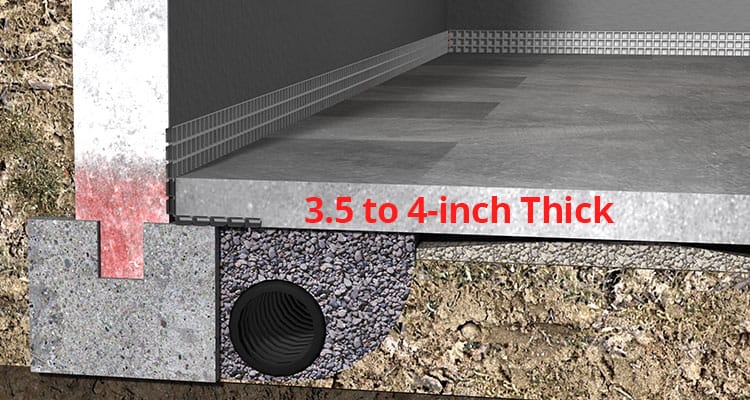

If you complete your basement into supplemental living room for your residence, you are going to want to do away with the concrete floors by putting down some kind of cellar floor coverings. Do not settle for any downstairs room flooring ideas that don't fit your general picture for everything you need finished.
Fixing a Concrete Basement Floor American Dry
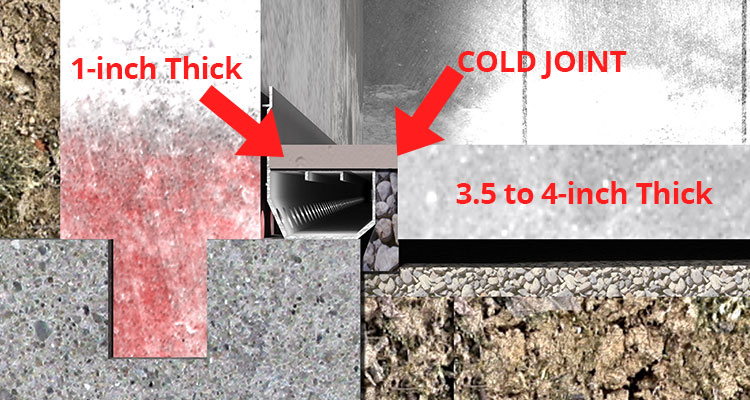
That can be an incredibly challenging aspect when choosing the correct flooring for your basement since almost all of the supplies are porous but at levels that are various. This makes flooring choices especially sparse because the flooring must be mold-resistant and resilient ; this generally rules out tile and carpet.
Images Related to How Thick Are Basement Floors
Concrete Floor Slabs Concrete Construction Magazine

BA-0309: Renovating Your Basement Building Science Corporation

How to pour a basement slab

Best Basement Flooring Options
/basement-flooring-1821693-PSD-V5-49348cb1c6da402a84016234b9b51f09.png)
Acceptable Tolerances for Residential Basement Slabs For
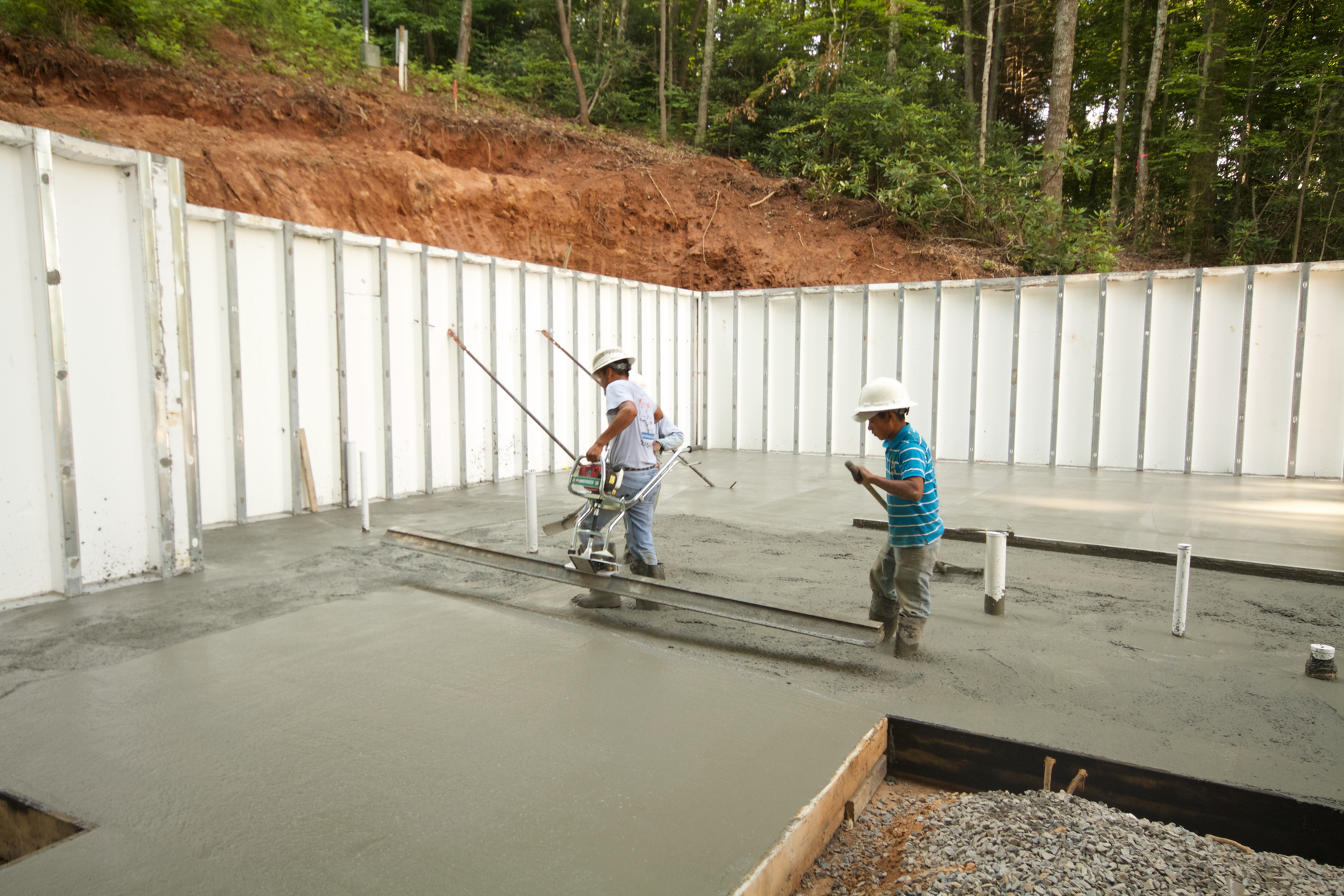

How to Find How Thick Your Concrete Slab Is

Building Guidelines Drawings. Section B: Concrete Construction
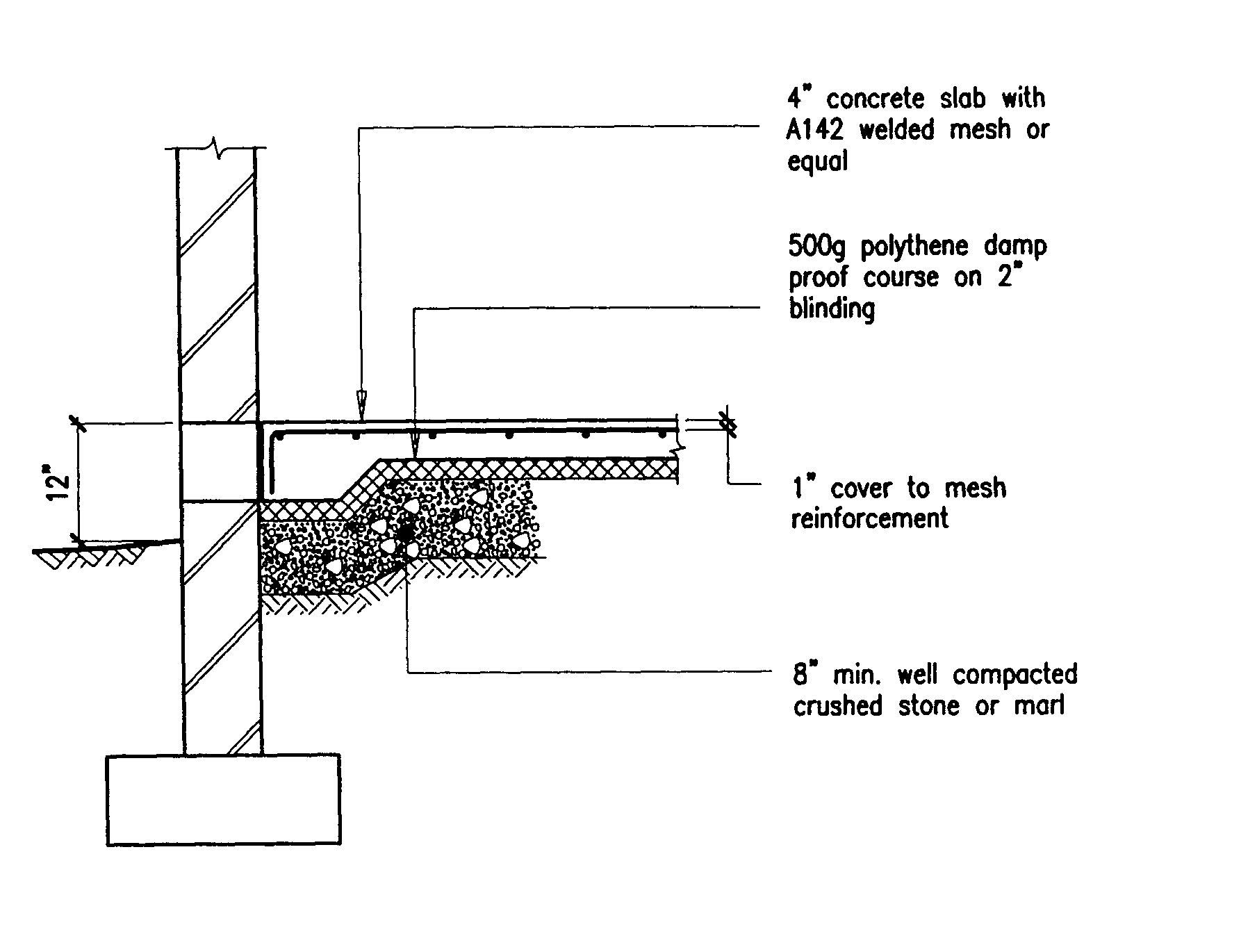
Baseboard Basement Drain Pipe System in Greater Cincinnati, OH
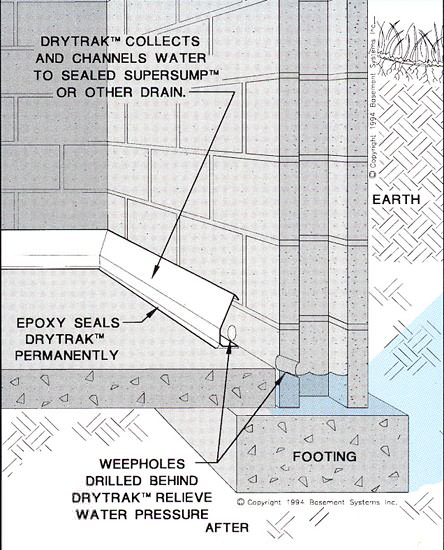
Fixing a Concrete Basement Floor American Dry

Concrete: Slab Thickness » Alpha Paving
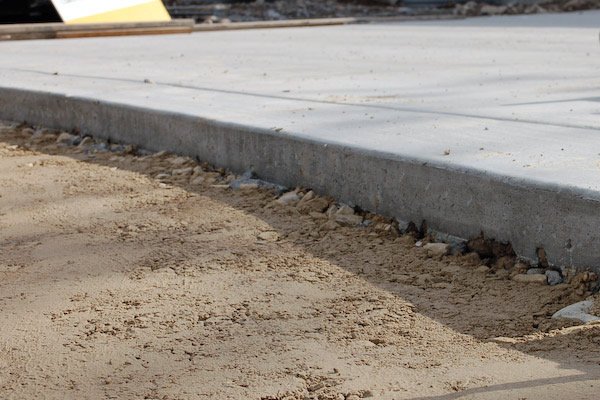

Fixing a Concrete Basement Floor American Dry
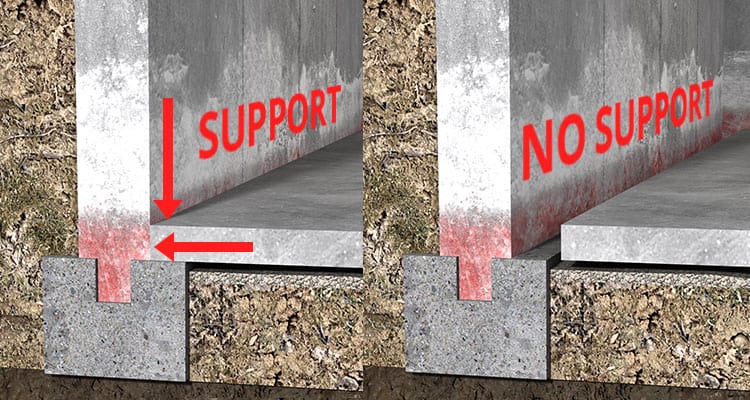
Dropping the Level of a Basement Floor JLC Online

Related articles:
- Basement Concrete Floor Sweating
- Basement Floor Finishing Ideas
- Painting Unfinished Basement Floor
- Unique Basement Flooring
- Basement Floor Epoxy And Sealer
- Brick Basement Floor
- Finished Basement Floor Plan Ideas
- Basement Floor Finishing Options
- Basement Floor Tile Ideas
- Concrete Basement Floor Finishing Options
How Thick Are Basement Floors: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
When it comes to constructing a basement, one of the key considerations is the thickness of the basement floor. The thickness of a basement floor depends on various factors, including load-bearing requirements, soil conditions, and intended use of the space. In this article, we will delve into the details of basement floor thickness, exploring different subheadings to provide you with a comprehensive understanding.
1. Factors Affecting Basement Floor Thickness:
The thickness of a basement floor can vary based on several factors. These factors include the type of soil, the load-bearing requirements, and the intended use of the space. Let’s take a closer look at each of these factors:
a) Type of Soil:
The type of soil on which your basement is built plays a crucial role in determining the thickness of the floor. If you have stable, well-compacted soil, you may require a thinner floor compared to areas with expansive or poorly compacted soil. Expansive soils tend to expand and contract with changing moisture levels, putting pressure on the basement floor. In such cases, a thicker floor is necessary to withstand these movements.
FAQ: Why is it important to consider soil type when determining basement floor thickness?
Answer: Considering the soil type helps ensure that the basement floor can adequately support the weight of the structure above and resist potential soil movements.
b) Load-Bearing Requirements:
Another significant factor influencing basement floor thickness is the load-bearing requirements. If your basement is meant to support heavy equipment or serve as a storage space for heavy items, a thicker floor will be necessary to prevent cracking or structural damage. Conversely, if your basement will only be used for light storage or recreational purposes, a thinner floor may suffice.
FAQ: Can I reduce basement floor thickness if I don’t plan on storing heavy items?
Answer: While reducing thickness might be possible in some cases, it is essential to consult with a structural engineer or building professional to ensure the floor can adequately support the intended load without compromising its integrity.
c) Intended Use of the Space:
The purpose for which you plan to use your basement also affects the required thickness of the floor. If you intend to convert your basement into a livable space, such as a bedroom or home office, it will require a thicker floor to meet building code requirements and provide proper insulation. On the other hand, if your basement will primarily serve as a storage area or laundry room, a thinner floor may be acceptable.
FAQ: Why does a livable space require a thicker basement floor?
Answer: A thicker floor ensures proper insulation and soundproofing, providing comfort and meeting building code requirements for habitable spaces.
2. Typical Basement Floor Thickness:
While basement floor thickness can vary based on specific circumstances, there are typical ranges that can guide your decision-making process. These ranges are influenced by industry standards and local building codes. Let’s explore these ranges according to different scenarios:
a) Residential Basements:
In most residential settings, where basements are used for general purposes like recreational areas or storage, the typical basement floor thickness ranges from 3 to 4 inches (7.6 to 10.2 cm). This thickness is sufficient to support light loads and provide adequate durability.
FAQ: Is it possible to have a thinner basement floor in a residential setting?
Answer: While there might be some cases where local building codes allow for thinner floors, it is crucial to consult with professionals familiar with local regulations to ensure Compliance and structural integrity. In general, it is recommended to follow the typical thickness ranges to ensure a safe and durable basement floor.
b) Commercial or Industrial Basements:
In commercial or industrial settings where the basement will be subject to heavier loads, the typical basement floor thickness ranges from 4 to 6 inches (10.2 to 15.2 cm). This increased thickness helps provide additional strength and durability to withstand the higher load-bearing requirements of these spaces.
c) Below-grade Living Spaces:
If you plan to convert your basement into a livable space, such as a bedroom or home office, the typical basement floor thickness may need to be thicker. Building codes often require a minimum thickness of 4 inches (10.2 cm) for below-grade living spaces to ensure proper insulation, soundproofing, and structural stability.
It is important to note that these are general guidelines, and specific circumstances may require adjustments to the basement floor thickness. Factors such as soil conditions, load-bearing requirements, and intended use of the space should always be considered when determining the appropriate thickness for your basement floor. Consulting with professionals, such as structural engineers or building contractors, can help ensure that you make informed decisions based on your specific situation. The thickness of a basement floor depends on the intended use of the space and local building codes. In general, for residential basements used for general purposes like recreational areas or storage, a typical thickness is 3 to 4 inches (7.6 to 10.2 cm). Thicker floors ranging from 4 to 6 inches (10.2 to 15.2 cm) are recommended for commercial or industrial basements that will be subject to heavier loads. If you plan to convert your basement into a livable space, such as a bedroom or home office, a minimum thickness of 4 inches (10.2 cm) is often required to ensure proper insulation, soundproofing, and structural stability. It is important to consult with professionals familiar with local regulations and consider factors like soil conditions and load-bearing requirements when determining the appropriate thickness for your basement floor. Overall, it is important to consult with professionals familiar with local regulations and consider factors such as soil conditions, load-bearing requirements, and intended use of the space when determining the appropriate thickness for your basement floor. This will ensure that you meet all safety and durability requirements for your specific situation.