You will have a convenient subfloor for epoxy, tile, carpeting, or maybe whatever area you want if you ever get tired of the blank concrete flooring appear. This undoubtedly turns into the explanation why the demand for polished concrete floors these days has skyrocketed, and folks are opting for it as an economical and innovative choice outdoor & indoor.
Here are Images about Concrete Floor Slab Design Guide
Concrete Floor Slab Design Guide
Polished concrete floors are an excellent strategy of flooring which are more and more becoming a way of life for many home as well as business people. Polished concrete floor surfaces also have a number of advantages making them an environmentally friendly, affordable and practical method for apartments and housing. In house and shop settings, concrete floor is also less noisy than floorboards of flooring.
Reinforced Concrete Slab Design Guidelines – The Constructor

A polished concrete floor does not need to have frequent cleaning, which means that you can clear them alternatively or whenever you're absolutely free. Concrete is very long-lasting and hardly ever has to be replaced though you could have to touch up the finish that's an inexpensive and easy pretty job. Along with these benefits, one of the major benefits of concrete floors is its pricing. It is important to install a vapor barrier in the concrete to prevent moisture and radon gas from penetrating the concrete.
Images Related to Concrete Floor Slab Design Guide
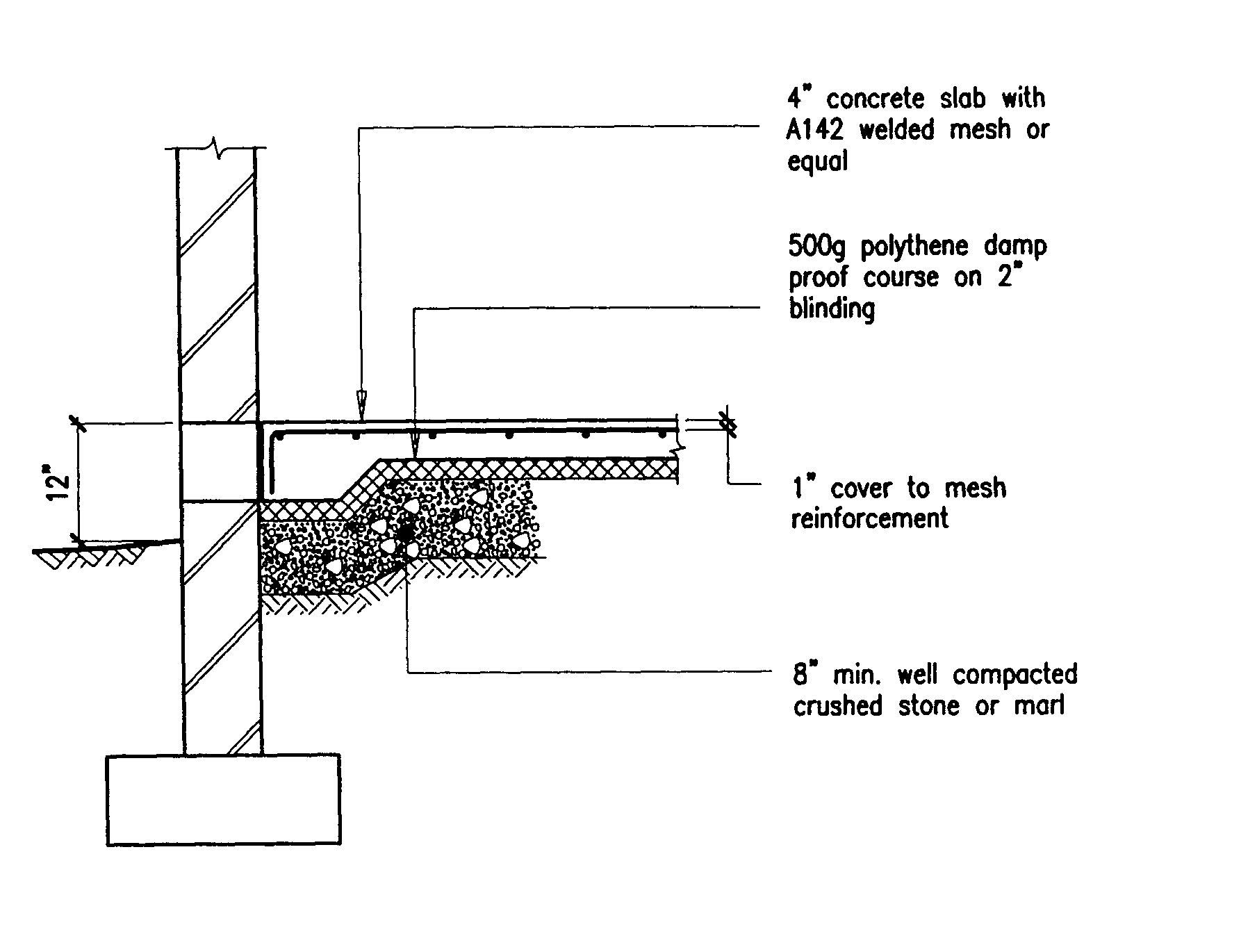
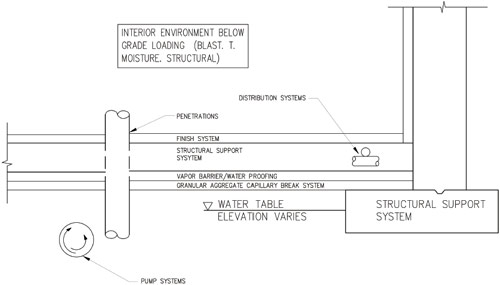
Building Guidelines Drawings. Section B: Concrete Construction
Building Guidelines Drawings. Section B: Concrete Construction
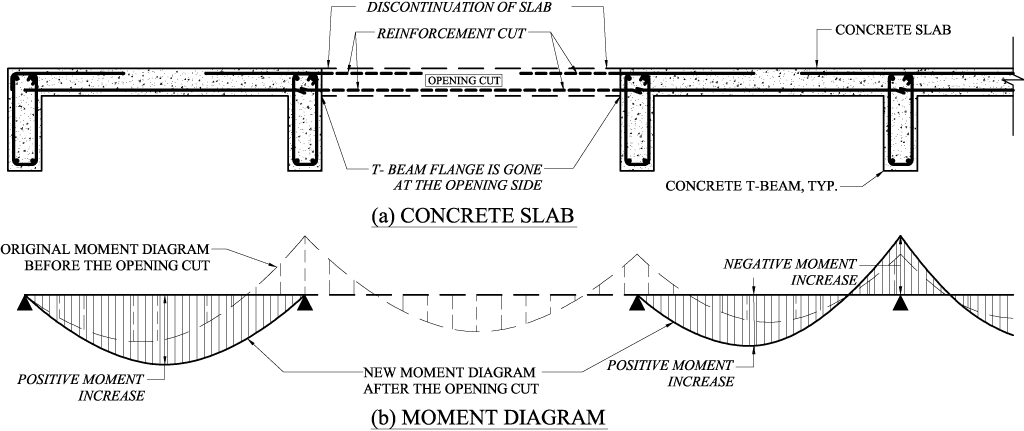
STRUCTURE magazine Creating an Opening in Existing Floors
Floor Slabs WBDG – Whole Building Design Guide
How to Design One-way Slab as per ACI 318-19? Example Included

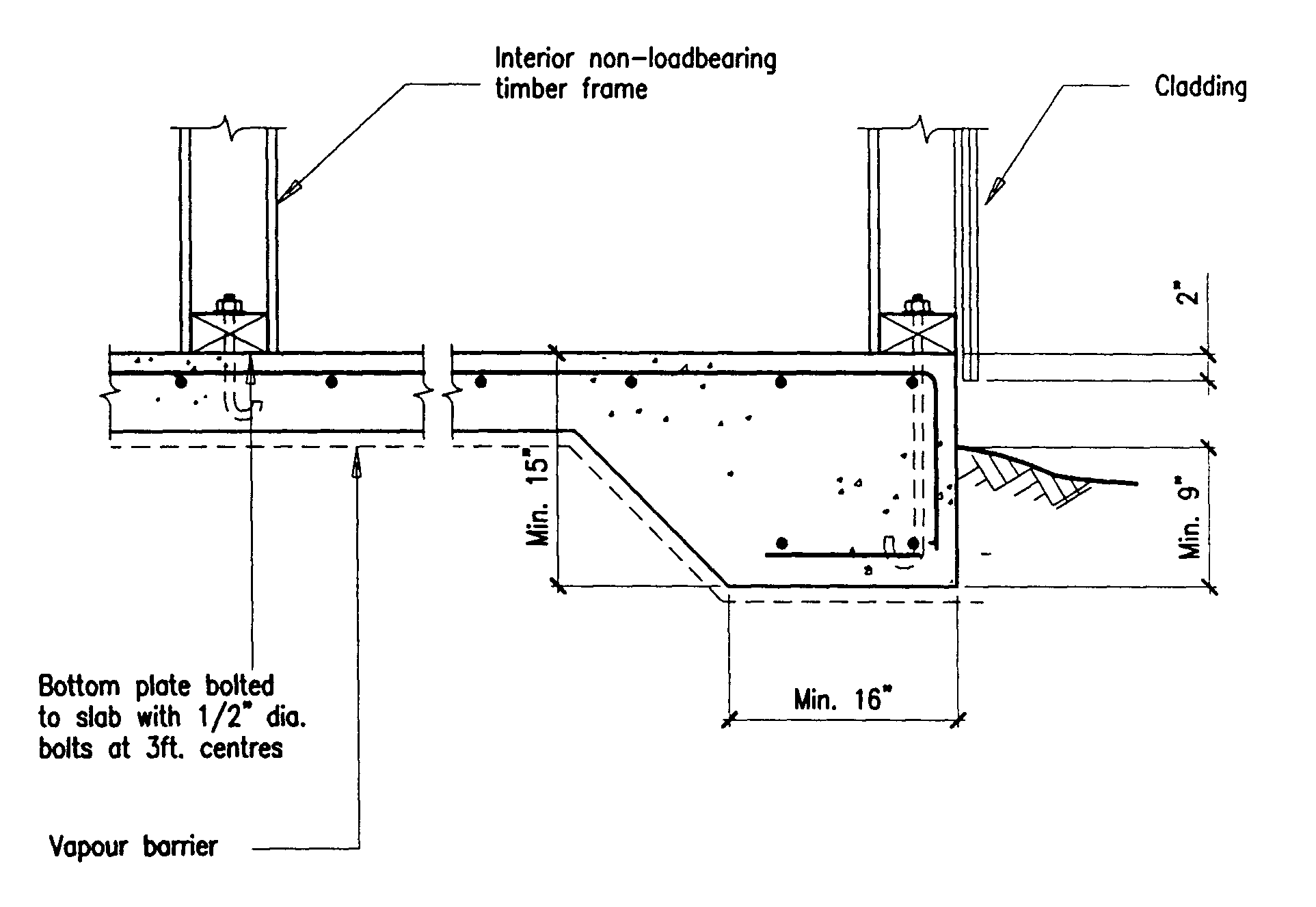
Building Guidelines Drawings. Section B: Concrete Construction
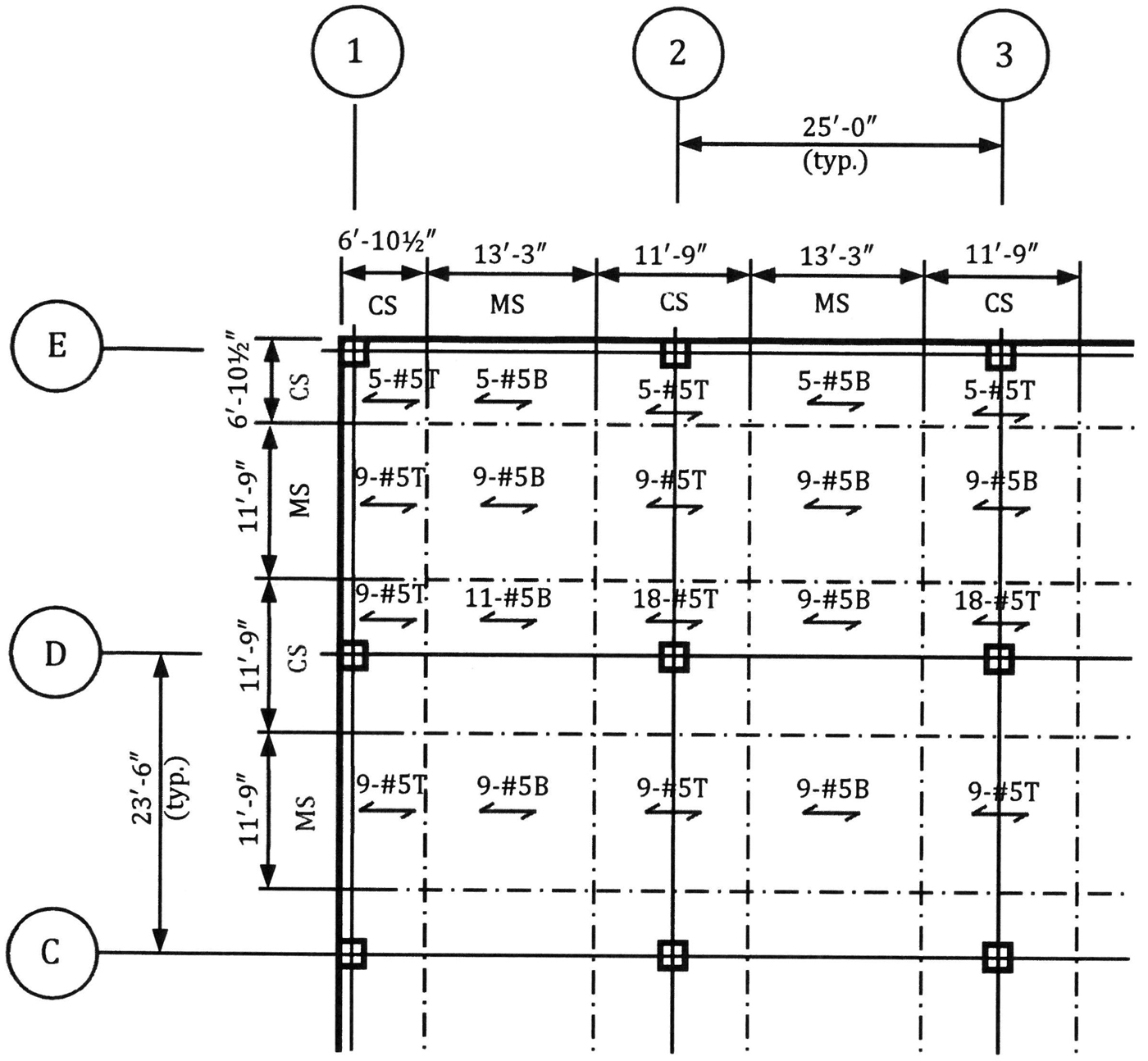
STRUCTURE magazine Recommended Details for Reinforced Concrete
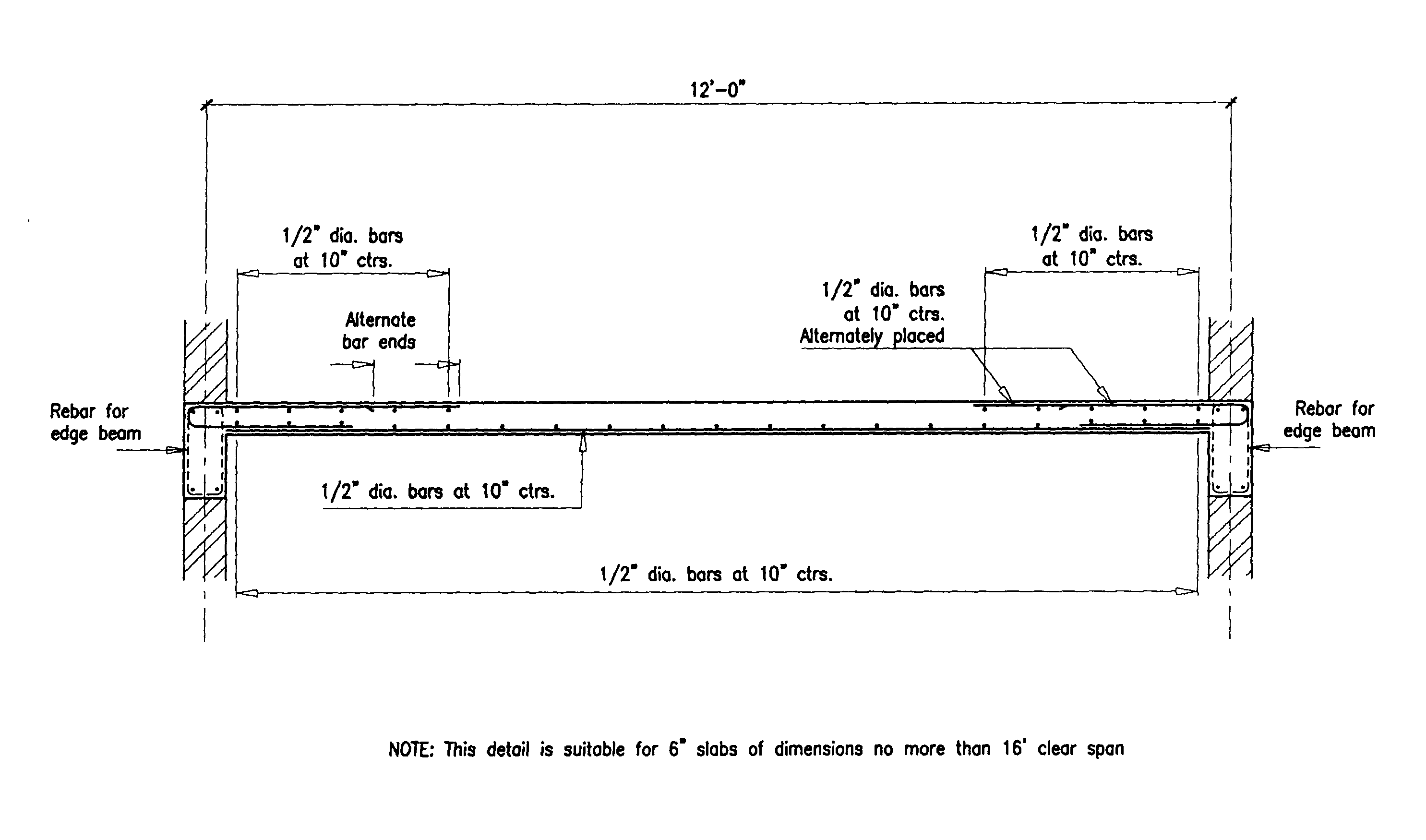
Concrete Floor Slab Reinforcement Example
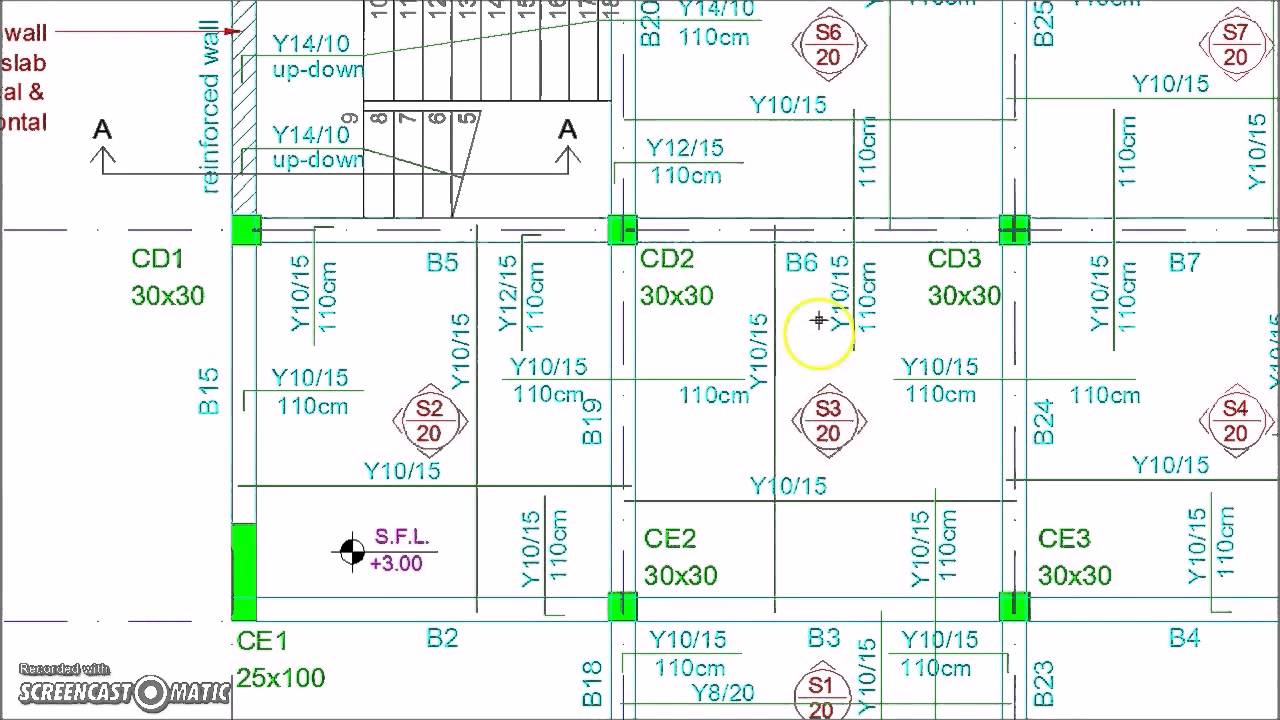
Working with Design of a Reinforcement Concrete Slab

Two-Way Concrete Slab with Beams Spanning Between Supports
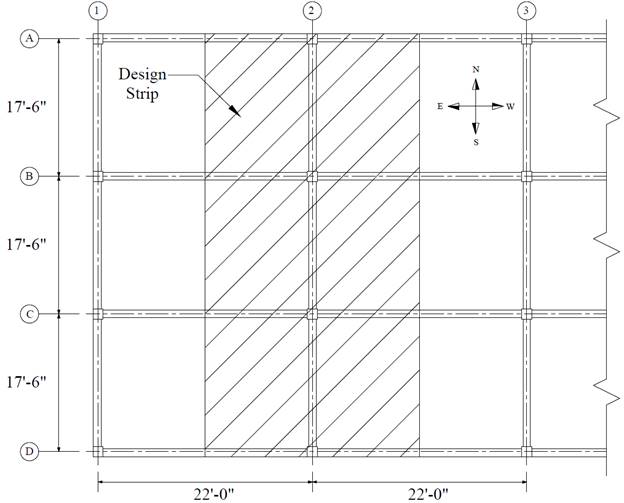
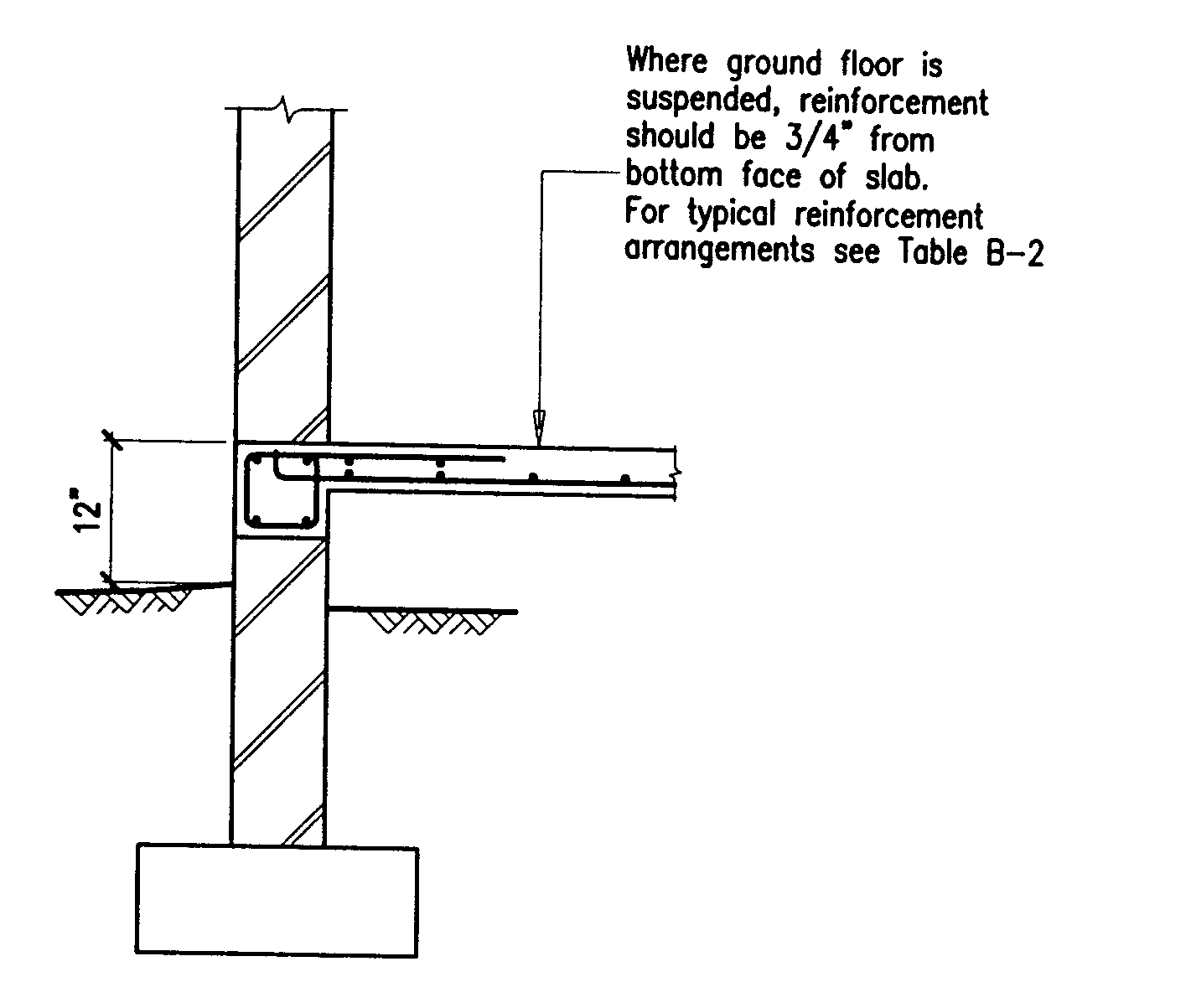
Building Guidelines Drawings. Section B: Concrete Construction
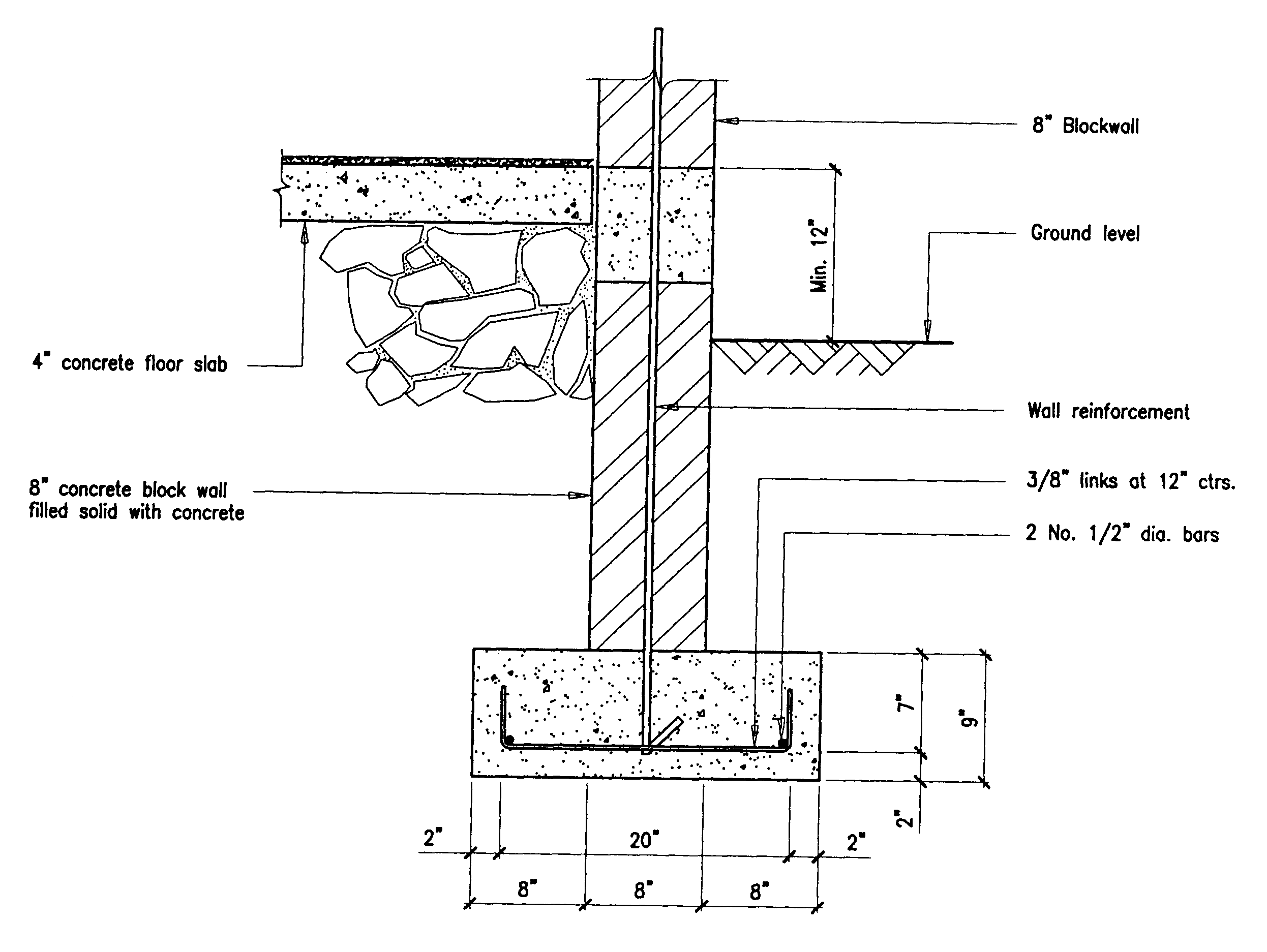
Concrete Floor Slabs Concrete Construction Magazine

Related articles:
- White Mold On Concrete Floor
- Polished Concrete Floor
- Polished Concrete Floor Cleaning
- Staining Concrete Floors Indoors Yourself
- Flooring Options For Concrete Floors
- White High Gloss Concrete Floors
- Acid Stain Concrete Floors DIY
- Redo Patio Concrete Floor
- Interior Concrete Floor Ideas
- Gloss Concrete Floor Paint
Designing a concrete floor slab is a complex process that requires careful planning and consideration of many factors. The design of a concrete floor slab is determined by its intended use, the subgrade soil conditions, the load-bearing capacity of the foundation, and other structural considerations. In this guide, we will discuss the essential elements of designing a concrete floor slab and how to properly plan for it.
What Is a Concrete Floor Slab?
A concrete floor slab is a flat surface constructed from concrete, typically found in basements, garages, and other areas with limited space. It is designed to evenly distribute loads on the foundation and provide a level surface for foot traffic and other activities.
Subgrade Soil Conditions
The condition of the soil beneath the concrete floor slab plays an important role in the design process. The soil must be assessed to determine its ability to support the weight of the slab and any additional loads placed on it. Compaction tests are often used to measure the soil’s bearing capacity and help inform the design decisions.
Load-Bearing Capacity of Foundation
The load-bearing capacity of the foundation must also be taken into account when designing a concrete floor slab. The foundation must be able to support not only the weight of the slab but also any additional loads placed on it, such as furniture or equipment.
Design Considerations
When designing a concrete floor slab, there are several key considerations that need to be taken into account, such as:
– Thickness: The thickness of the slab should be determined based on the intended use and the load-bearing capacity of the foundation. Generally, thicker slabs are recommended for areas that will experience heavier loads or more frequent foot traffic.
– Joints: Expansion joints, control joints, and construction joints should all be considered when designing a concrete floor slab. These joints help reduce cracking by allowing for thermal expansion and contraction, as well as accommodating any movement caused by settling.
– Reinforcement: Steel reinforcement bars are often used to increase the strength and durability of a concrete floor slab. The type and amount of reinforcement used should be based on soil conditions, load bearing capacity, and other design considerations.
– Finishes: The finish applied to a concrete floor slab can affect its appearance and performance. Common finishes include paint, sealants, epoxy coatings, staining, polishing, and more.
Conclusion
Designing a concrete floor slab requires careful planning and consideration of many factors. Subgrade soil conditions, load-bearing capacity of the foundation, thickness of the slab, joints, reinforcement, and finishes should all be taken into account when designing a concrete floor slab. With proper planning and consideration of these factors, you can ensure that your concrete floor slab is safe and durable for years to come.