more and More homeowners and designers are building basements and warehouses with concrete due to the appearance, the natural beauty, the easiness in maintenance as well as the warmth it brings to an area. The method is very simple to use with state-of-the-art technology. In case you walk into a put that has polished concrete floors, you will realize instantly that the place is somewhat akin to marble.
Here are Images about Building Regs For Concrete Floor Slab
Building Regs For Concrete Floor Slab

Polishing might be put on to the majority of audio concrete floors. Apparently, a small floor area to be dealt with might only take a brief period of time to carry out while an even greater area may be finished after an extended time period. These are embedded into the floor using a saw so the design options are really versatile.
Concrete Floors and Replacing a Timber Floor with Concrete After
Today's concrete for floor surfaces comes in a broad range of colors that are different, and it is doable to include in a variety of different stone and other components to create a polished concrete floor a point of attractiveness. Concrete flooring has great appeal for people excited about environmentally friendly construction.
Images Related to Building Regs For Concrete Floor Slab
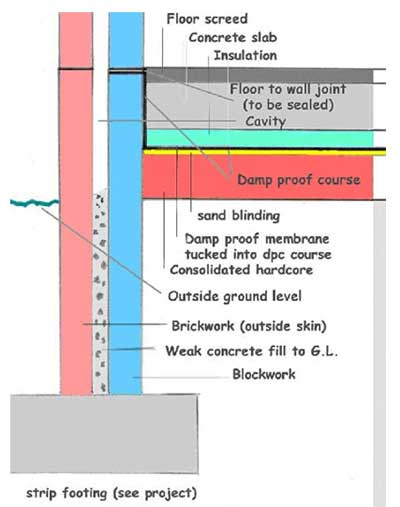
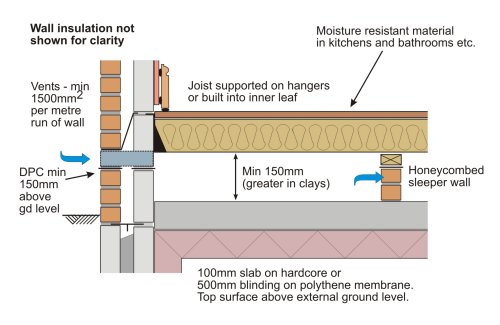
E5MCPF23 Concrete Ground Bearing Floor, Insulation Below Slab LABC

Detail Post: Floor Details – First In Architecture

Strip Foundation Ground Floor Cavity Wall Interactive 3D Detail

E5SMEW25 Concrete Ground Bearing Floor, Insulation below Slab LABC

GreenSpec: Housing Retrofit: Ground Floor Insulation
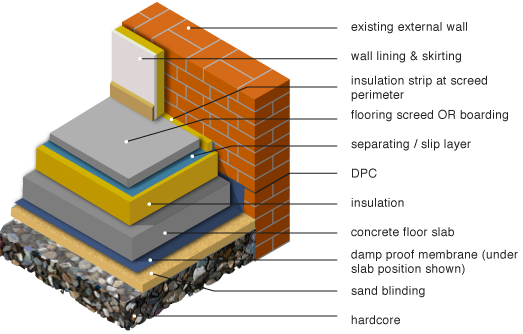
How To Insulate An Existing Concrete Slab? BagOfConcrete
Evolution of Building Elements
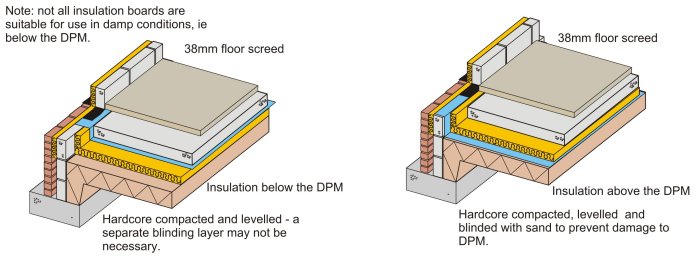
Ground Bearing Floor Slab – 650×368 PNG Download – PNGkit

Concrete Floor Slabs Concrete Construction Magazine
Borders Underfloor Heating supply water filled underfloor heating

Limecrete Floor Systems Glasscrete Insulating Floors

Evolution of Building Elements
Related articles:
- Concrete Floor Cleaning Machines For Rent
- Best Epoxy Concrete Floor Paint
- Concrete Floor Interior House
- Concrete Flooring Pretoria
- Concrete Floor Coverings For Patios
- Concrete Floor Stain Pictures
- Behr Concrete Floor Sealer
- Stained Concrete Floor Tiles
- Gray Concrete Floor Paint
- How To Paint Old Concrete Floor
Building Regulations for Concrete Floor Slabs
When it comes to constructing a building, one of the most crucial elements to consider is the floor slab. The concrete floor slab provides a solid foundation for the entire structure and must be built according to specific building regulations to ensure its strength, durability, and safety. In this article, we will delve into the various building regulations that govern the construction of concrete floor slabs.
Subgrade Preparation
Before pouring concrete for a floor slab, it is essential to properly prepare the subgrade. The subgrade refers to the natural soil or compacted fill material that supports the concrete slab. Building regulations require that the subgrade be adequately compacted and leveled to prevent settlement and cracking of the slab over time. Additionally, a vapor barrier may be required to prevent moisture from seeping up through the subgrade and causing damage to the concrete.
FAQs:
Q: Do I need to install a vapor barrier under my concrete floor slab?
A: In most cases, building regulations recommend installing a vapor barrier to protect the concrete from moisture damage. However, this requirement may vary depending on local codes and environmental factors.
Concrete Mix Design
The strength and durability of a concrete floor slab depend significantly on the quality of the concrete mix used. Building regulations specify minimum requirements for the compressive strength of concrete used in floor slabs to ensure that it can withstand the intended loads and environmental conditions. The mix design must also take into account factors such as aggregate size, water-cement ratio, and admixtures to achieve the desired properties of the concrete.
FAQs:
Q: What is the minimum compressive strength required for concrete floor slabs?
A: Building regulations typically require a minimum compressive strength of 3000 psi for interior floor slabs and 4000 psi for exterior slabs exposed to weathering.
Reinforcement
In some cases, building regulations may require additional reinforcement in concrete floor slabs to enhance their structural integrity. Reinforcement can take the form of steel rebar or fibers added to the concrete mix to increase tensile strength and reduce cracking. The spacing, size, and placement of reinforcement bars must comply with building codes to ensure proper distribution of load and prevent failure under heavy loads.
FAQs:
Q: Do all concrete floor slabs need reinforcement?
A: Not all floor slabs require reinforcement, but it is generally recommended for larger or heavily loaded slabs to improve their strength and durability.
Joint Placement
Another critical aspect of building regulations for concrete floor slabs is joint placement. Joints are installed in the slab to control cracking caused by shrinkage, temperature changes, or settling of the subgrade. Building codes specify the spacing, depth, and type of joints required based on factors such as slab thickness, expected loads, and environmental conditions.
FAQs:
Q: How far apart should control joints be placed in a concrete floor slab?
A: Control joints are typically spaced at intervals equal to 24-36 times the thickness of the slab. However, this spacing may vary based on specific project requirements and local building codes.
Surface Finish
The surface finish of a concrete floor slab not only affects its appearance but also its functionality and maintenance requirements. Building regulations may specify minimum standards for surface finishes based on factors such as slip resistance, abrasion resistance, and ease of cleaning. Common surface finishes include troweled smooth finish, broom finish, exposed aggregate finish, or polished finish.
FAQs:
Q: What is the Recommended surface finish for a concrete floor slab in a high-traffic area?
A: In high-traffic areas, a broom finish or exposed aggregate finish is often recommended for better slip resistance and durability.
Overall, compliance with building regulations for concrete floor slabs is essential to ensure the structural integrity, durability, and safety of the structure. It is important to work with a qualified engineer or contractor to design and construct concrete floor slabs that meet all relevant building codes and standards. Failure to comply with regulations can result in costly repairs, structural failures, and safety hazards. By following the guidelines outlined in building regulations, you can ensure that your concrete floor slab will perform effectively and withstand the intended use for years to come. Additionally, proper maintenance and regular inspections are crucial to ensure the longevity of concrete floor slabs. Any signs of damage, cracking, or deterioration should be addressed promptly to prevent further issues. By following building regulations and implementing proper maintenance practices, you can extend the lifespan of your concrete floor slabs and maintain a safe and functional environment for occupants.